What is SEO?
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the act of making improvements to your website’s content, authority, and user-friendliness in order to positively impact its performance in the search results of Google, YouTube, and Bing.
Specifically, SEO is about increasing a website’s rank in search results to get organic traffic (website visitors from unpaid search results).
Why is SEO Important?

There are about 200 million active websites out of the billions of websites in existence. The popular ones are only a tiny fraction of that 200 million. A majority of websites are not known.
SEO helps you get known by placing your website in front of potential customers who are looking for your product or service or asking related questions.
Here are some more reasons why you need SEO:
- People trust search engines, and showing up high on Search Engine Result Pages (SERPs) increases the trust level of your website, meaning the possibility of you converting is higher.
- SEO can help prove you are a market knowledge leader and put you ahead of your competition.
- Depending on your product/service, you can reach hundreds of thousands of searchers monthly.
- SEO has 20 times more traffic opportunities than PPC.
How does SEO work?
Google and other search engines have bots that crawl websites on the internet to understand what the pages are about.
After crawling, they will add the allowed pages to their database (index) so that if a user searches using a relevant term, such pages can appear in search results.
To give weight to your page over similar ones, search engines quantify the quality and relevancy of your content and the authoritativeness of your website using several metrics, otherwise called ranking factors.
To do SEO, you must optimize your website based on those ranking factors.
Google’s Ranking Factors
There are over 200 known ranking factors. It’s so much to keep track of, and hardly anyone knows all of it.
What you should bother about are these core actions:
- Write great content: Ensure users get all the relevant and quality information about that topic from the article or page. Google emphasizes this in most update announcements.
- Gain authority and trust: Publish content that other websites find relevant to gain backlinks and use other link-building tactics to garner backlinks.
- Format your website and content for bot and user-friendliness: This involves several actions, from having mobile-friendly and fast websites to writing content that is easy to understand.
There are several factors to SEO, but if you do the above three, you are 80% closer to the first page of search results.
Let’s look at SEO in-depth using these five categories:
- Technical
- On-page
- Off-page
- Local
- International
Technical SEO
Technical SEO covers what you should do to ensure search engine bots can crawl and index your website. It also includes optimization for user-friendliness, including how interactive your website is and how fast it loads.
Here are some technical SEO areas to focus on:
- Crawlability and indexability
- Duplicate pages
- Core web vitals
- Structured data markup
- Security
- Canonicals
- Website architecture
- Mobile-friendliness
Crawlability and Indexability
You need an XML sitemap and a robots.txt file to ensure you get the right pages on search results.

An XML sitemap helps search engines discover the pages you want them to index.
When starting an SEO project for an old website, first check if your website is on Google by searching with “site:yourdomain” to see if you can find any results.
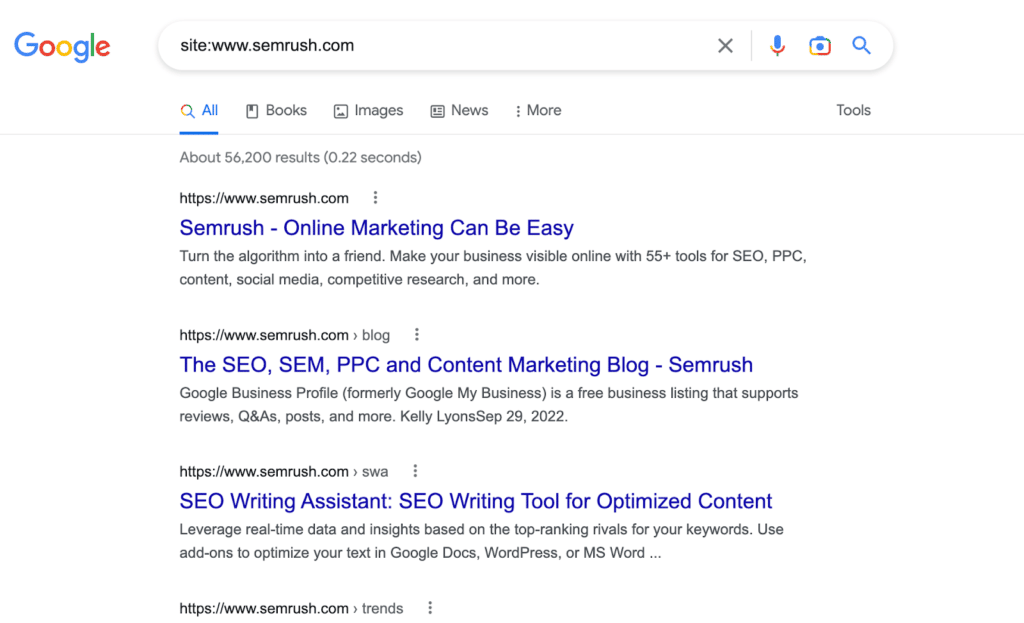
If there are no pages or the number of results is less than the number of pages you have, you have indexing issues.
Now, check for a sitemap; you can find most sitemaps in the /sitemap.xml directory. Enter “https://yourdomain/sitemap.xml” in your browser.

If you can’t find a sitemap, you should create one. You can learn how to in our SEO course.
When done creating your sitemap, you should submit it to Google Search Console.
Apart from the sitemap, you will need a robots.txt file. A robots.txt file tells search engines the pages you don’t want them to crawl.
You can also use your robots.txt to point search engines to your sitemap. This is important if you fail to submit the sitemap directly.
Duplicate Pages
Duplicate pages affect the indexability of your website. Having duplicate pages can confuse search engines on which page to index for the target keyword.
To avoid showing the wrong version to searchers, you should implement redirects or canonical tags.
Canonical URLs are used if you have two or more pages with the same content to tell search engines which one best represents the group of duplicates.
A Redirect is used if you want to point one page to another temporarily or permanently. It is best used if you delete a page and want users who visit that page to be served something relevant or if you are doing temporary work like maintenance on your site.
Core Web Vitals
Core web vitals (CWV) are metrics that quantify user experience based on the loading time of your page, how stable your content is as it loads, and how easy or sweet it is to interact on your page.
CWV is more than just a ranking factor; it can also influence how many sales or leads your website gets.
Think of it: if you get on a website and it’s slow, or you click on one button and another responds instead, you will leave as quickly as you came in.
To score well for core web vitals, you need to use compressed Javascript, lazy-loaded images, modern images (WebP), and several other specifics. We have written a guide on core web vitals to help you get started.
Structured Data Markup
Google is all about satisfying the intent of the searcher. Structured data is one of the ways they do that.
Structured data is information formatted using code to give search engines better context about a page so they can return richer results which can boost your click-through rate.
For example, if you have a recipe on your page, you can use structured data to let Google know so you can show up like this in search results:
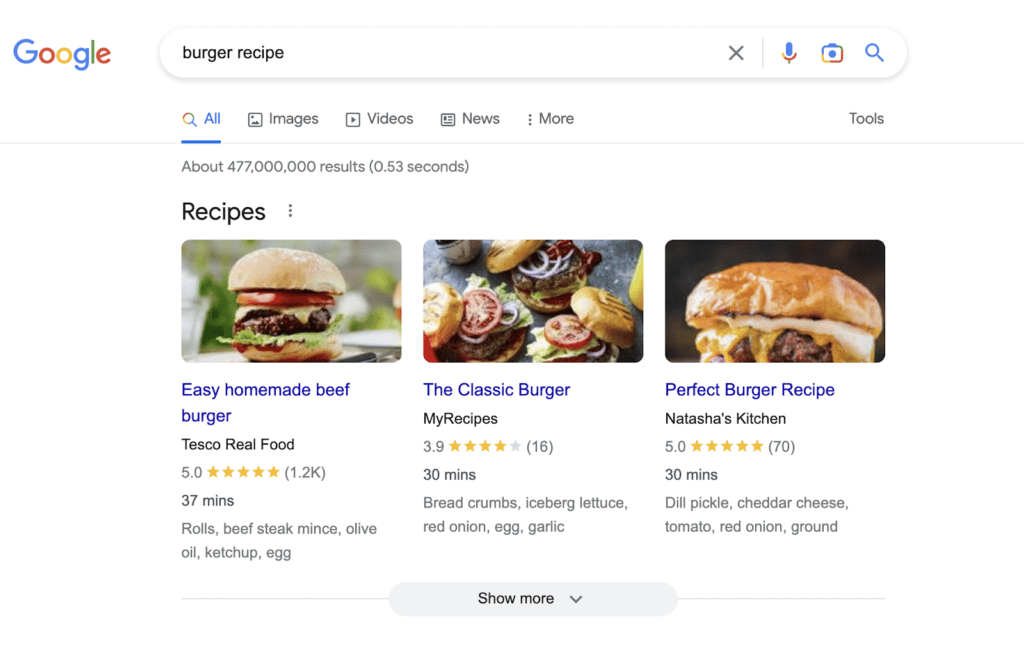
You can mark up several things, including organization, reviews, products, and courses.
Schema markup is the language or code for implementing structured data. You can start learning all about it on schema.org, the online encyclopedia for schema markup.
If you are not tech-savvy, writing schema markup code will be hard. Google’s structured data tool and Merkle’s Schema Mark-up Generator are nice tools to avoid manually writing code.
You can also look at our ultimate guide to structured data.
Security
Security is important to search engines; they want users to be satisfied. One aspect is ensuring that users are not getting viruses or having their information stolen when they visit your website.
HTTPS is a ranking signal for Google. HTTPS shows that you have secured data on your website through an SSL certificate and HTTPS in force.
Also, Google shames websites with expired SSL certificates and insecure content with an obvious warning in search results that says, “this site may harm your computer”.
Browsers also provide warnings.
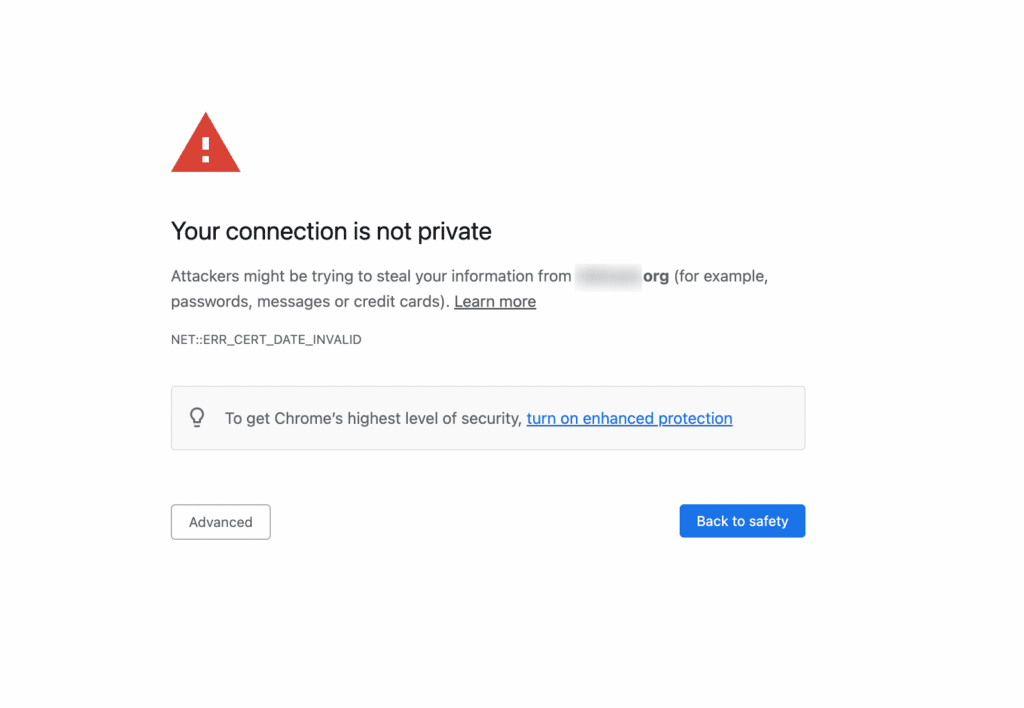
In addition, poor website security puts you at a greater risk of hacking, which can tank your SEO efforts if the hacker places terrible content or spammy links on your website.
Search engines can pick up on spam and may add warning labels to your listing in search results or backlist your website, depending on the severity of your security issues. Even if you clean up your site afterward, it will take some time to recover rankings.
To prevent adverse results, ensure you have security features on your website and server, ranging from brute force protection to firewalls.
Security can also affect your reputation. If you sell online and users are shown a “not secure” warning, they will likely leave your website.
Website Architecture
Website architecture has to do with how pages are organized on your website.
What you do with your architecture can affect how well search engines can crawl your website, especially when you have 100 or more pages.
A good website architecture ensures new pages are not several clicks away from your homepage to enable good crawling and value (link equity) shared from existing pages.
For good architecture, there are some quick wins you can do today, all detailed below.
Ensure it’s easy to navigate different parts of your website. A good menu structure can make this possible.
Every page must have existing pages linking to them. Do not leave any page floating around; floating pages are called “orphan pages” in SEO. Orphan pages are not easily found by search engines and people.
Use breadcrumbs to show users where they are on your website.
Another win you can schedule is to design a helpful 404 error page. These are shown to visitors who end up on a page that is missing or deleted.
URL Structure
Your URLs are part of your architecture.
First, do not have pages placed too deep in subfolders. For example, rather than https://home.com/one-category/another-category/another-category/another-category/web-page, keep things simple with at most two or three levels, for instance, https://home.com/one-category/another-category/web-page (three levels). The closer a page is to the home page, the better.
Also, use descriptive URLs; for example, https://example.com/women/black-shoe is good, while https://example.com/folder/page-0200393 is bad.
Lastly, use the right URL structure: this means using lowercase all through, hyphens rather than underscores, and including your keyword in your URL.
Mobile-friendliness
Since 2016, Google has primarily used the mobile page version for indexing and ranking.
Also, a majority of searches are done on mobile devices. Therefore, you must optimize your website not only for desktops but also for mobile phones. Ensure that all your pages are mobile responsive, made to load fast, and work well on mobile devices.
Google Search Console has a section that details pages with elements that aren’t mobile responsive. Use that but also check manually to be proactive.
On-page SEO
On-page SEO covers areas of optimization that deal with what happens on a page or content and what led to creating the content. It covers the process from finding the right topic to publishing it right.
Here are key on-page SEO areas:
- Keyword research
- Content writing & optimization
- Page title and meta description
- Image alt text and accessibility
- Content structure
- Internal links
- E-A-T
Keyword Research
Keyword research is the process of discovering terms that your target audience uses when searching for your products, services, or questions related to your products/services.
There are two phases to keyword research:
- Finding keywords for your service/product pages.
- Discovering questions your target customers are asking and creating articles around them.
Find Keywords for Your Product or Service Pages
Make a list of terms that you think a potential customer will use when searching on Google for your product or service.
If you don’t know where to start, you can use Google Search or the search feature on big e-commerce marketplaces like Amazon to get phrases. The auto-complete feature in the search bar provides suggestions based on what people have searched.
Take those suggestions to a keyword research tool like Semrush or Ahrefs to see if there are searches for that phrase.
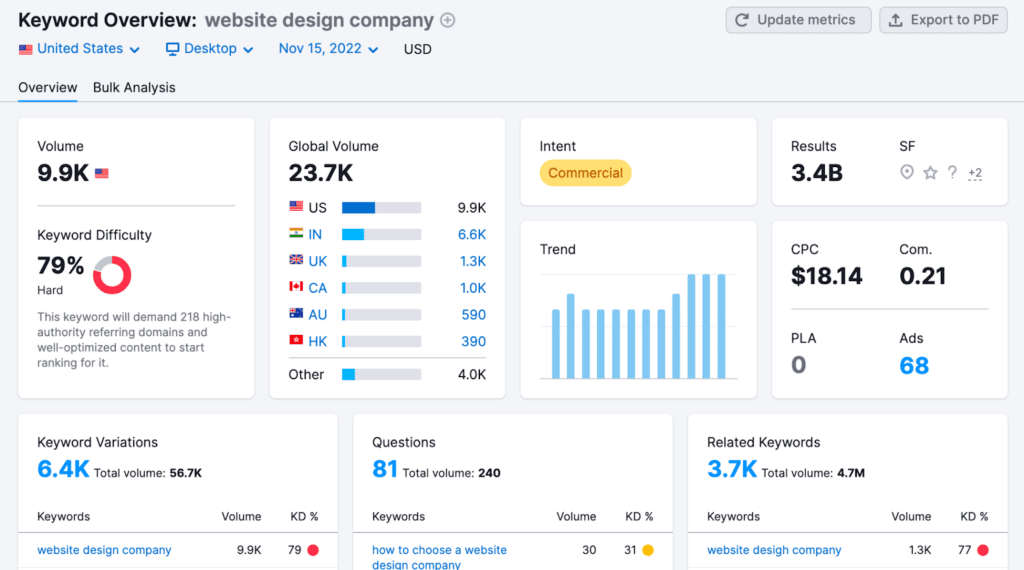
Take a look at the data in the Semrush keyword magic tool to see if there are keywords with more searches than the one you put in and to find additional keywords.
If using Ahrefs, also check the top keyword or parent keyword section to see the best keyword related to what you have imputed.
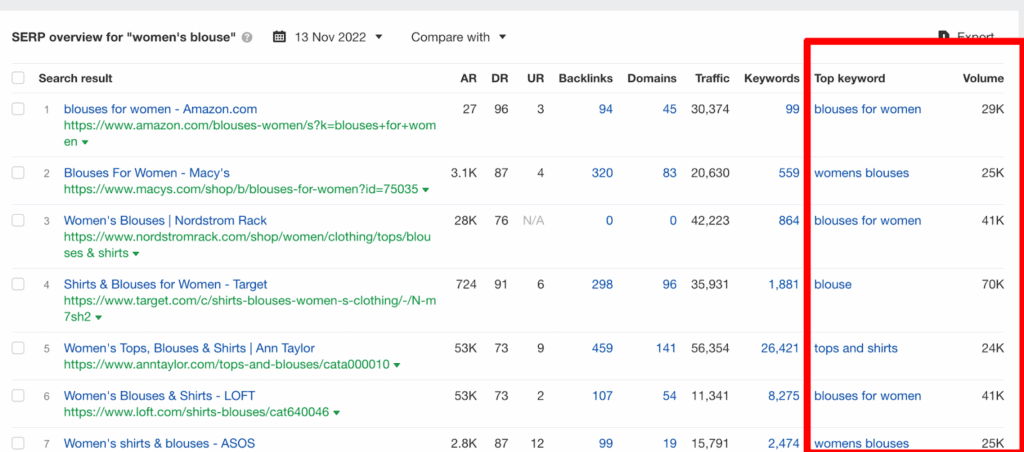
Finding Keywords for Blog Posts
Here are some methods you can use to find keywords or topic ideas for blog posts.
- Use the data from the keyword overview, particularly the Questions and Related Keywords, to find phrases that work.
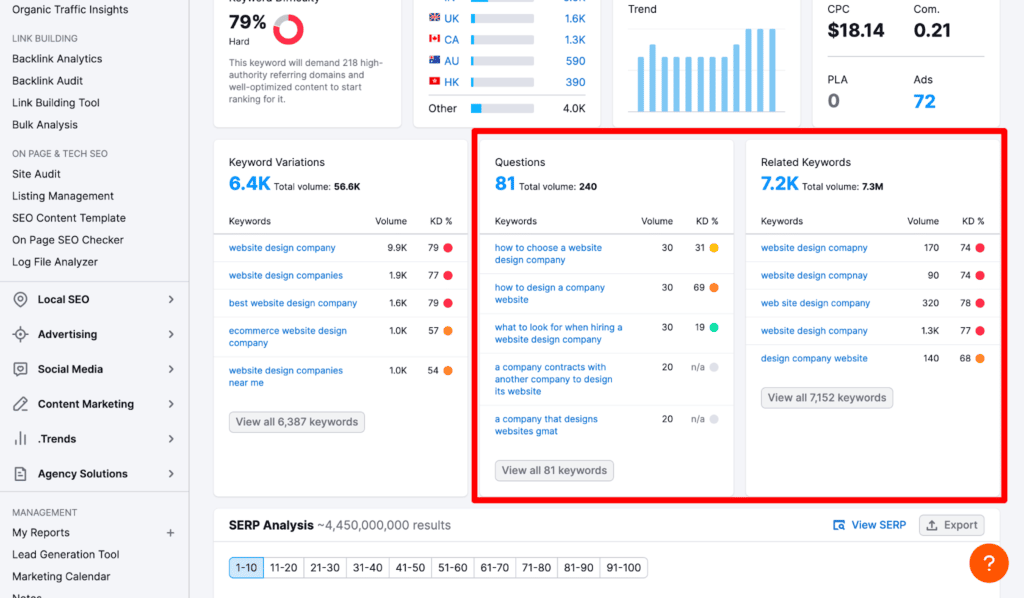
- Add your domain and competitors’ domains in Semrush’s keyword gap tool to find the keywords they are ranking for, but your website isn’t. You may be able to find keywords that are suitable for blog posts and those that are suitable for service/product pages.
- Paste a few of the keywords found from your product/service keyword research in Google Search and look at the “People Also Ask” section for questions you can create blog posts around.
Choosing Keywords
You may find a lot of keywords from your research process; not all of them will be worth pursuing from the start.
These questions can guide you when choosing keywords:
- Is the keyword’s search intent in line with what you are doing and your goals?: Search intent, in simple terms, means why the searcher searched. That can be to
- Gain information (informational intent – keywords like what, why, how-to).
- To compare products (commercial intent – keywords such as Mailchimp vs. ConstantContact).
- To buy something (transactional intent – keywords like “buy” and “where to buy”).
- To find a page on a website (navigational intent – keywords such as “Facebook login” or include “Reddit”).
To know what the search intent is, check the search results for the type of pages that are ranking. Also, the keyword overview tool shows the intent of a keyword.
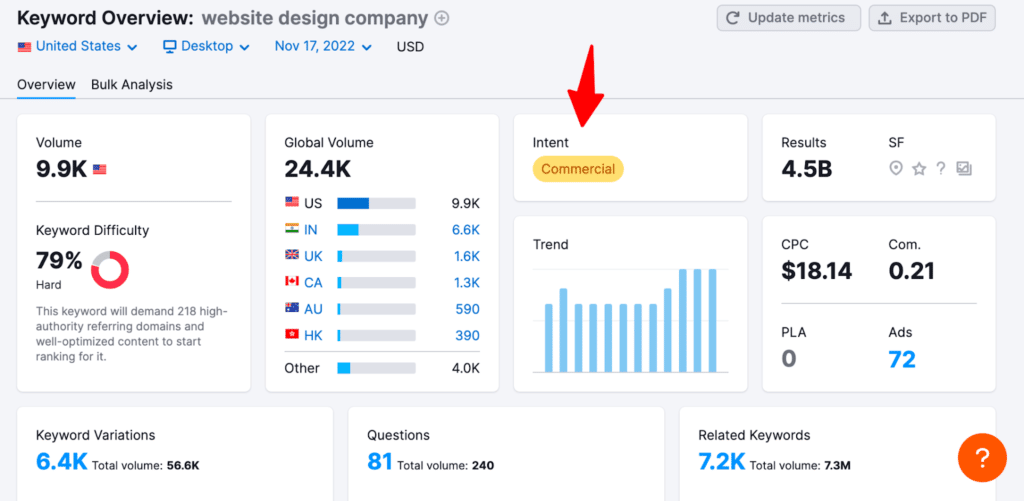
- Is the keyword difficulty (KD) low enough?: KD is how hard it will be to rank based on an evaluation of the competitors currently in the search engine results.
- For a new website with no traffic or backlinks, choosing a keyword with a difficulty of 90 is ambitious; it’s unlikely you will rank for this term. However, if your domain authority or authority score is 50-100, a difficulty of 90 may work.
- Nevertheless, you can rank well for a high-difficulty keyword if you provide the best content.
- Is there a decent search volume for the keyword?: Search volume is an estimate of the number of searches made per month using that keyword. The sweet point for search volume depends on your location and industry. For some locations, a keyword with at least 1000 monthly searches is better to invest in for returns than one with a few hundred monthly searches. However, for local businesses in small cities, a volume of 300 is good.
- Can you match or provide better content for the keyword than what your competitor has?: If you cannot provide better content or more value than what’s already on the first page of Google search results, you may not be able to rank on that page.
When done, you should have several keywords to use. Start with your core product/service pages and two to five blog posts, and schedule the others in a content calendar.
Content Writing & Optimization
Getting a great keyword is just the first step. How you use them matters. This part is one of the most misunderstood parts of SEO.
Contrary to what many may think, content optimization is not about using your keywords a set number of times in your article. Depending on how you do that, your content will either be flagged (for keyword stuffing) or not rank because you haven’t given enough signals for relevancy and quality. Use the tips below instead.
Satisfy the Searcher
Before you start writing, check what’s in Google search results. What are your competitors writing about? If the results are filled with product pages, a blog post is unlikely to rank for that term.
When you have verified, you can write for the searcher’s intent, check what is missing in your competitors’ content, and note that down for your content.
Also, check the People Also Ask section to see if there are any questions that could add value to your post.
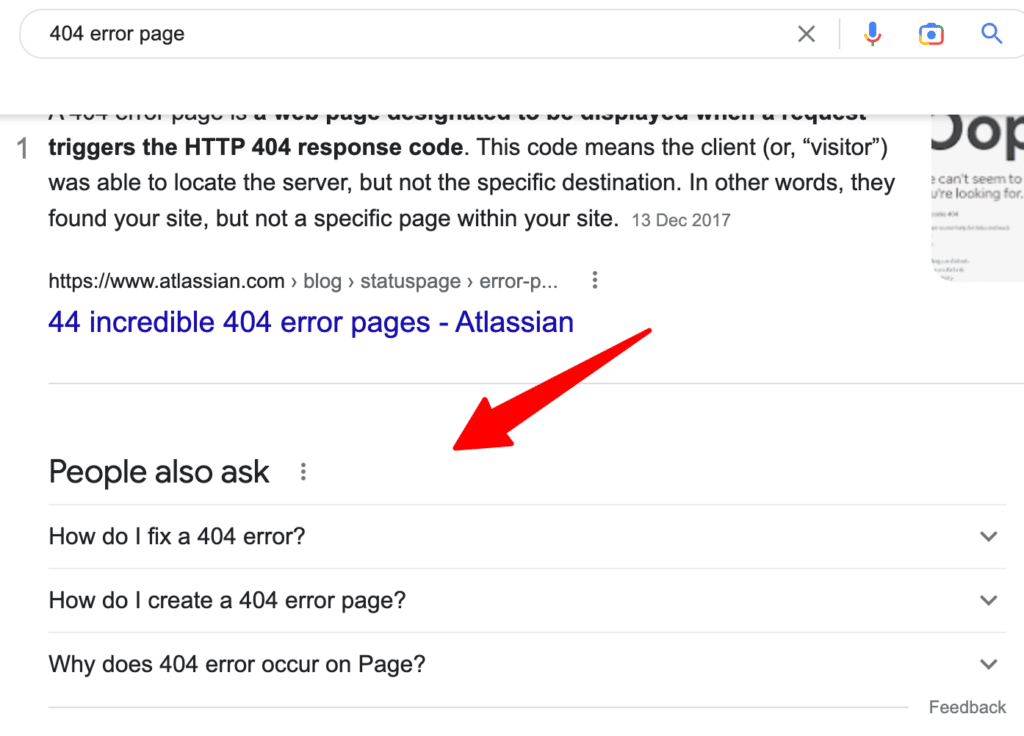
Brainstorm other areas to add to satisfy and engage the searcher better. That can be some storytelling in-between, some infographics or relevant images, stats, etc.
Write to ensure that the searcher does not have any lingering questions on that topic after reading your post. In doing this, you must ensure you write too much and end up with a book rather than an article.
If there are many subtopics in one article that can stand alone as separate articles, provide an actionable overview in your post and link to another article that will be an in-depth look at that topic. For example, with this post, I could have easily written 20,000 words as there is a lot to write about SEO, but I provided links to other topics covering the different SEO areas/terms.
Remove Unnecessary Words
When writing blog posts, one thing you should do is cut out lengthy, drawn-out introductions unless you are telling a captivating story that your target audience likes.
If you are looking for a DIY guide, you don’t want to have to dig through an 8-paragraph introduction and several other unnecessary paragraphs in the rest of the content. Your website visitors feel the same way.
Answering the question of the user/the search intent early on makes for better SEO. Also, lengthy introductions can cause visitors to leave or bounce quickly.
Furthermore, do not add fluff or unnecessary words just because you want to hit a word count. There is no perfect word count for every topic. What you write should be based on what can satisfy the searcher.
Write Naturally
Do not force your keywords in your content; write naturally. When you write good-value and quality content without bothering about keywords, in most cases, you would include the keywords naturally.
Writing naturally also ensures you include semantically related phrases. These are keywords that are conceptually linked to your keyword. They give more context to search engines on what your article is about. For example, if you are writing a post on wedding dresses, bride, cake, and shoes may be semantically related phrases.
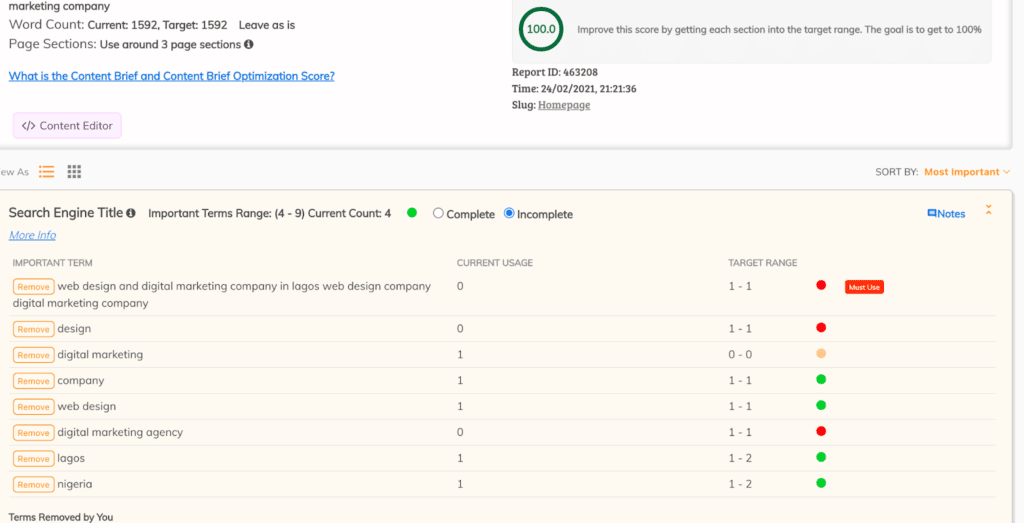
After writing, you can run your content through tools like Surfer’s Content Editor or Page Optimizer Pro to check if you have added most of the relevant semantically related phrases. At this point, you can try adding them if it makes sense and can fit naturally.
Content Structure
The best content structure for SEO allows users to skim your articles and still get value.
Most people do not read the entirety of a page. Make it easy for readers to find what they want by giving them the following:
- Table of contents: if sticky, even better.
- Few paragraphs per sub-heading: if the paragraphs under each subheading aren’t broken by bullets or visual content, keep them to a maximum of 6-8 paragraphs.
- Numbered and bulleted sections.
- Short paragraphs and sentences: most of your paragraphs should be 2-3 lines. Shorter sentences relay information better.
- Images and videos: posts with visual content increase engagement by 180%.
- Heading tags in your content: this is heading one to heading 6 (H1 to H6). Use heading one for your topic, heading 2 for sub-headings, heading 3 for sub-headings under heading 2, and so on. Include your keyword and related terms in your headings.
- Easy-to-read content.
Page Titles and Meta Description
The title tag and meta description can influence how many people click on your listing in search results.

Your title tag can influence your rankings, but your meta description does not affect your ranking. Nevertheless, your meta description can influence your click-through rate.
Beware that Google is often rewriting title tags, replacing them with the H1 or other text on the page. Also, Google may replace your meta description with a phrase on your page, depending on the search phrase used. It’s best you keep the title and description relevant to your article to reduce the chances of that happening.
Here are best practices:
- Include your keyword in your page title, but do not keyword stuff. Use a keyword while ensuring it is benefit-oriented to attract searchers.
- Write unique, descriptive, and accurate titles – include only relevant words.
- Your title should be similar to your H1.
- Keep title tags between 50 to 60 characters.
- Your meta description should be a summary of your content; a snippet from your content may work.
- Do not keyword-stuff your meta description.
- Keep your meta description between 150 to 160 characters.
- Every page should have a unique title and meta description.
Image ALT Text and Accessibility
Screen readers cannot describe an image to visually-impaired users or those who have turned off images. You must ensure you cater to visitors who cannot see your images.
You can do that by adding image alt texts. Here are tips for your image alt texts:
- Accessibility first before SEO: describe the image without trying to force in the keyword. Nevertheless, you may include your keyword or a term conceptually linked to the keyword, but only if it works naturally.
- Make it as succinct as possible but as detailed as needed: although there’s no character limit, it’s best to keep it short (30-200 characters) to avoid confusing listeners.
- Do not use single words: they typically do not describe anything.
- Alts should be related to the text on the page: Google sees the ALT texts as part of the text on a page, so ensure the image and its ALT are related to the paragraphs around them.
Internal links
Internal linking is one SEO area that floats between technical and on-page SEO. It has to do with adding links to your other web pages in your page.
It’s important to link to existing pages or posts on your website because it gives users easily-accessible information and tells Google that you have more quality content related to your page’s topic.
Also, internal links help Google crawl your website better and share link equity to your linked pages.
Always add links to relevant pages or articles in your content.
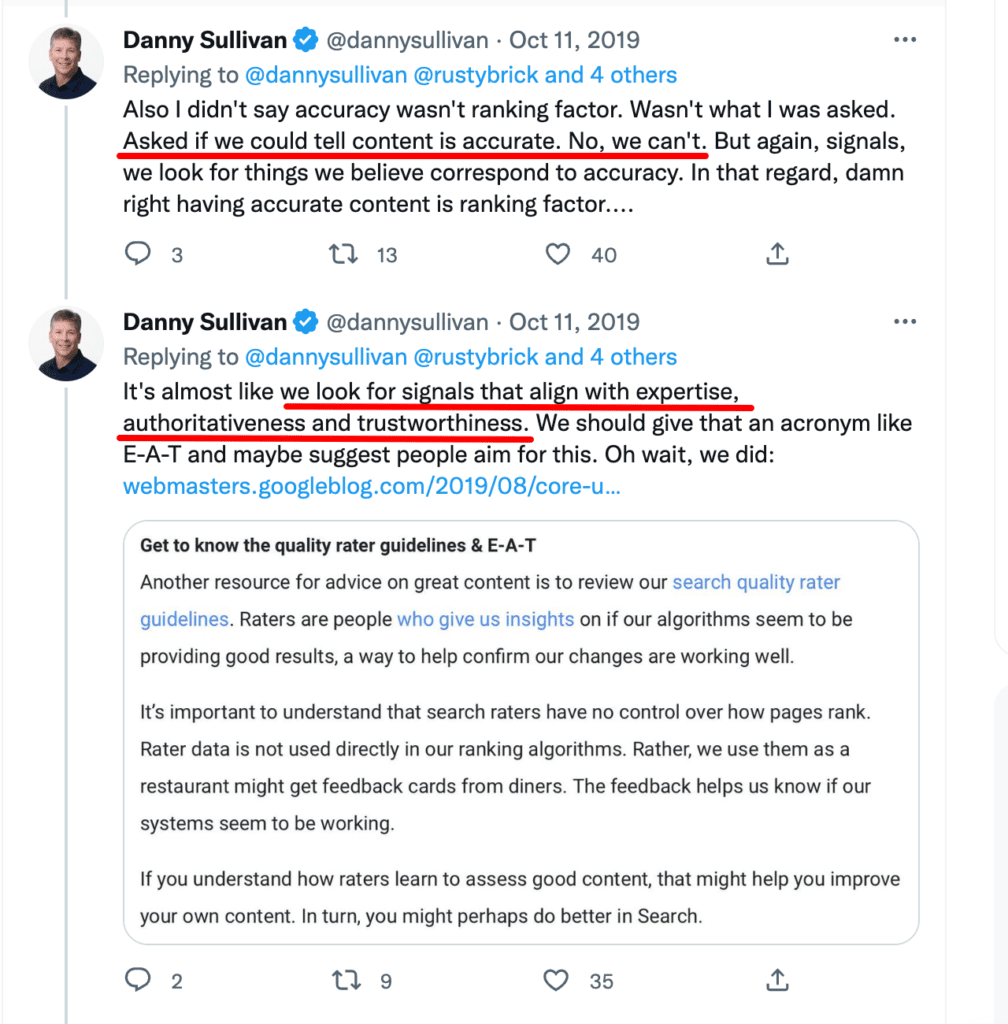
E-A-T
EAT stands for Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness.
Expertise deals with the creator of the content, while authoritativeness and trustworthiness have to do with the content creator, the content itself, and your website.
Search engines cannot verify the factual accuracy of every piece of content, so they use E-A-T to identify websites with high levels of expertise, authority, and trust.
To have a good E-A-T, implement the following:
- Have experts write your content.
- Include author sections in your articles with clear information on each author.
- Provide clear customer service information to help users resolve issues, especially if you sell online or are marketing a business.
- Use a secure connection on your website, including SSL, encrypted payments, etc.
- Write factually-accurate content.
- Tell users who you are; you can do this through an about page and good copywriting.
Off-page SEO
Off-page SEO encompasses the optimization you do outside your website to promote it. That primarily involves backlinks (link building).
Off-page SEO also includes brand mentions, social media marketing, and influencer marketing. However, these do not directly impact your organic rankings. Nevertheless, they may help you get more reach; for example, social media may help your content gain awareness which may result in some backlinks and visitors.
The goal of off-page SEO is to build your website authority and trust factor so you can rank higher for relevant terms with a quality article.
At the same time, off-page SEO can bring in customers, especially if you get a link or mention on a website that your target market also frequents.
For this section, we will take a look at link building only.
Link Building
Link building is the process of getting backlinks to your website. This is a crucial part of SEO; it’s like a thumbs up in your direction from other websites.
Backlinks can help you rank higher on Google if you get them from quality websites.
In short, if your links are from paid sources, spam websites, bots, link exchanges, or link farms, your ranking will be negatively affected.
There are many link-building strategies, including:
- Guest posts: publishing an article that includes your link on another website.
- Broken links: this involves finding links to a broken page on your website or a competitor’s page and requesting they be replaced with a live page on your website.
- Sponsorships: this includes getting a link on a website due to donations to a cause or partnership and publishing paid editorial posts.
- Link inserts: for this strategy, you would request a link to be inserted on an existing page, round-up post, or resource page.
- Partnerships: this includes reaching out to customers, business partners, associations, and other people you know to ask for a link.
How to do Link Building
There are many steps for link building, depending on your chosen tactic.
You could use the Semrush Link Building Tool to get prospects or check for websites linking to your competitors (backlink gap) and request a link using any relevant link-building strategy.
More importantly, you should focus equally or even more on creating quality content because quality content naturally generates links and shares, which will count positively for you.
Local SEO
Local SEO has to do with optimizing your business and website for local searches. It includes on-page, off-page, and technical SEO, but it also goes further with Google map listing, Bing places, and local citations.
For keyword research with local SEO, you are to focus on the location your business serves, whether a city, county, or country. For example, “women’s blouse in Manchester” rather than just “women’s blouse”.
Google Business Profile
Google Business Profile or Map listing is responsible for the businesses you find in Google search results when you add “near me” or a location to your search phrase.
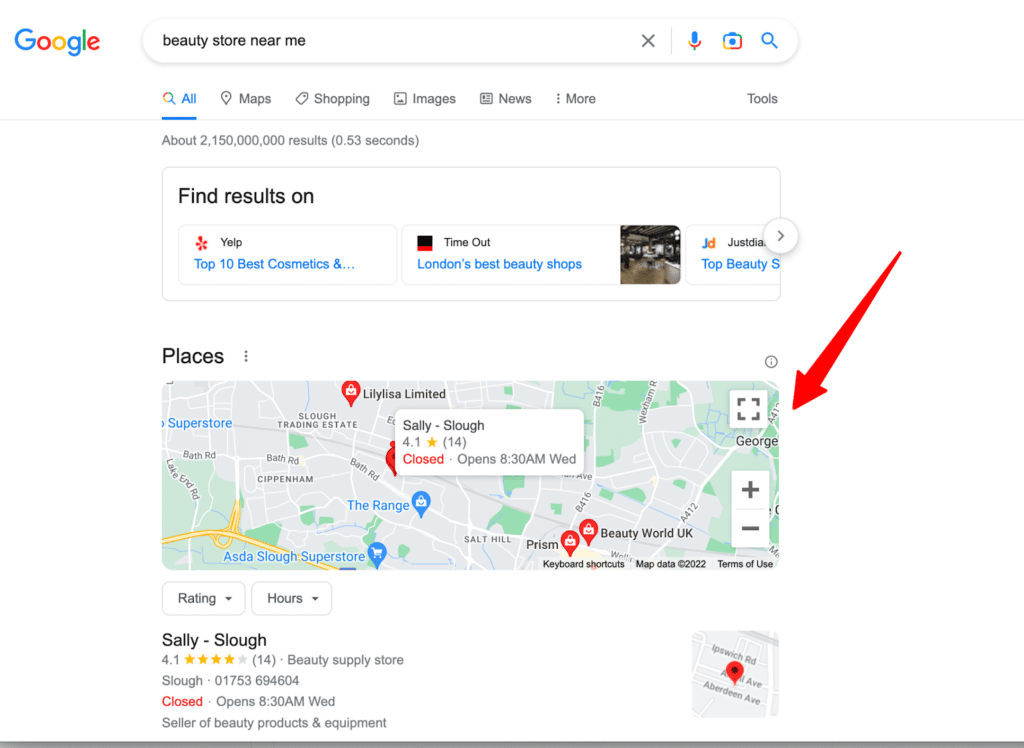
If you serve a specific location or have a physical office, you should add the business to the map and optimize your listing.
Google typically lists businesses in search results based on how close they are to the searcher, but they may also list businesses based on reviews and other specifics.
To be on the best track, you must aim for the top three organic results. 44% of people who perform local searches click on the first three results, and only 8% click on the load more button.
Take the following steps:
- Claim or create a listing on Google maps
- Provide the accurate category, correct address, phone number, and URL
- Use an optimized business description and list your services or products
- Add your hours
- Add images of the interior and exterior of your offices
- Encourage your customers to leave reviews
Local Citations/Directories
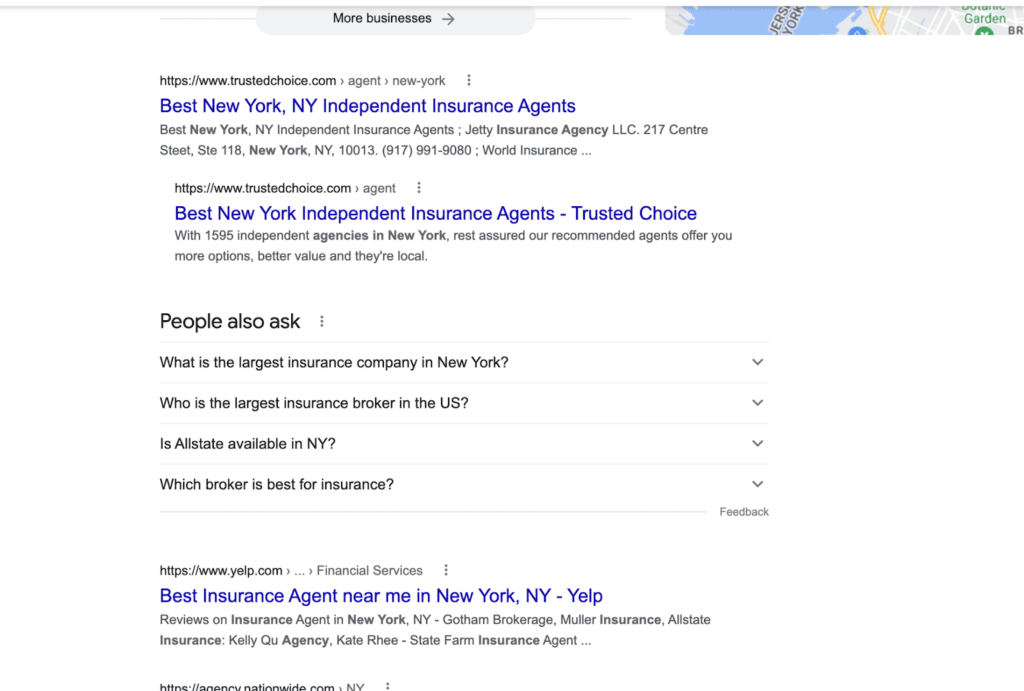
On searching Google for “insurance agents in new york”, the organic results on the first page are all directories. You must get on them to show up when your target audience searches and to tell Google that you are on platforms relevant to your industry and location.
You can start with international directories like Yelp that have location categories. Then, find directories that cater to your location and industry.
Ensure that your business’s name, address, and phone number (NAP) are consistent across all the online directories you are listed on, including your Google Business Profile. This is probably a ranking factor.
International SEO
Like local SEO, international SEO includes regular on-page, off-page, and technical SEO. The extra with this subset of SEO is the use of language and geographical targeting when dealing with multiple countries.
One great tactic to use when optimizing a website for a multi-national business is to have separate pages for each country they target.
However, to prevent keyword cannibalization (two pages targeting the same keyword) and Google showing the wrong pages to searchers, you should use Hreflang tags.
Hreflang Tags
Hreflang tags allow you to show search engines the relationship between your location-based pages. You can place them in HTML tags, the HTTP header, or the sitemap.
Here’s what hreflang tags in the HTML of a page look like:
- Rel means relationship
- X-default is the default or fall-back page if the searcher is in a country outside the other specified ones.
- Each country has its country and language code. For example, “en” stands for English, ZA stands for South Africa, and GB stands for the UK.
- Don’t specify a country all by itself; they must look like this – ”language-country code” – but you can specify a language alone.
You can learn more on our SEO course.
Measuring SEO Results
You should track your results to be sure your tactics are working.
First, set up Google Search Console. This has insights that show you what is working and issues with indexing, core web vitals, structured data, and mobile friendliness.
Apart from Google Search Console, you should also set up Google Analytics to track user behavior on your website and organic traffic. Through Google Analytics, you can tell if your traffic is going up or down.
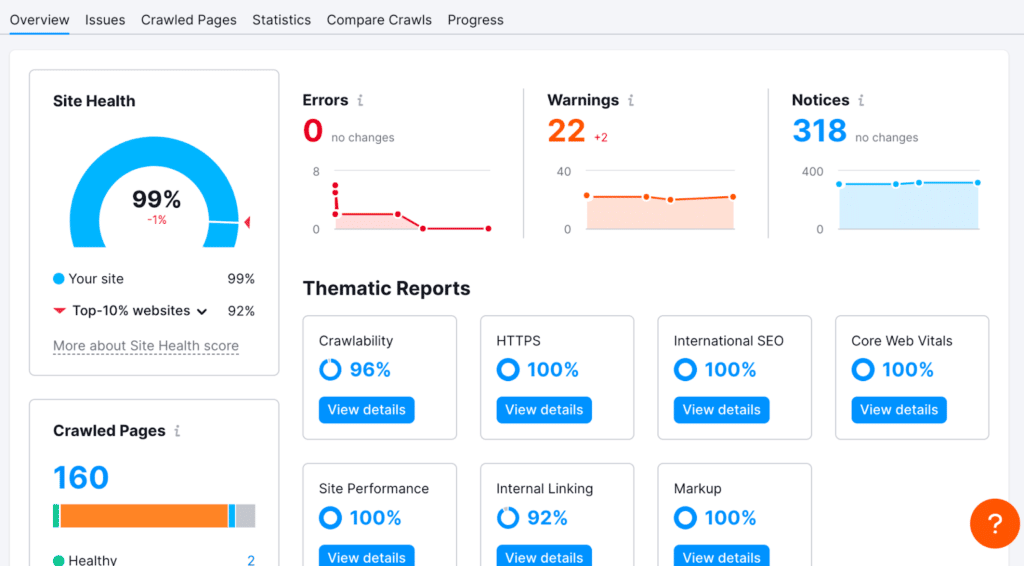
Lastly, you should have an SEO tool for tracking rankings and performing SEO audits to discover any issues that could affect indexing your site or your rankings.
Start Practicing
Learning SEO is more than reading SEO guides like this one. Practicing is best for retaining anything you have read.
Start today with some practice. That could be creating a sitemap and submitting it to Google or getting your hands dirty with keyword research. This SEO checklist can help you as you practice.
Lastly, SEO is an ongoing learning process. You shouldn’t stop here. Google implements updates every year, not to mention the many strategies you could uncover. You can subscribe to our newsletter to get more in-depth guides and take our Up-to-date SEO course that goes in-depth into all the above topics with support from top SEO specialists.
Whether you’re in Nigeria and are searching “what is SEO in Nigeria” or you’re in the US and are looking to learn SEO, we can help you.